S&P 500 Earnings Jump 5.1% as Tech Giants Miss Targets
Week Ending November 01, 2024
S&P 500 earnings surprised this week, jumping 5.1% YoY as big names in tech struggled to meet expectations. Across the Atlantic, the Eurozone economy doubled its growth pace to 0.4% in Q3, while inflation inched up to 2%, adding pressure to the ECB’s next moves. Meanwhile, China’s factory activity nudged into expansion, hitting 50.1 in PMI, yet exports showed lingering weakness. Dive into this week’s key takeaways and what they mean for investors.
🔍 Takeaway
This week, the global economy showcased its underlying contradictions. Strong corporate earnings in the U.S. clashed with shaky labor data, while Europe’s growth picked up even as inflation remained sticky. Emerging markets revealed both signs of resilience and underlying struggles, adding complexity to the global recovery narrative.
United States: Earnings for S&P 500 companies rose 5.1% YoY, buoyed by consumer strength, even as tech giants reported weaker-than-expected results. Meanwhile, October’s nonfarm payroll growth slowed drastically to just 12,000, the lowest since 2020, hinting at potential cooling in the labor market. These mixed signals could weigh on the Fed’s policy path as we look toward year-end.
International: Eurozone GDP grew by 0.4% in Q3, with Germany skirting recession and surprising economists. But inflation remains firm at 2%, posing a challenge for the ECB’s policy stance as they balance modest growth with persistent price pressures. Investors will be watching closely for signals on rate cuts or sustained tightening.
Emerging Markets: China’s PMI climbed above 50 to 50.1, signaling tentative recovery in manufacturing, yet export orders continued to decline, reflecting global demand challenges. Meanwhile, India’s growth resilience stands out, with robust PMIs consistently above 57, underscoring divergent paths within Asia. This contrast shows how policy and demand are shaping emerging market fortunes differently.
⭐️ Post of the week
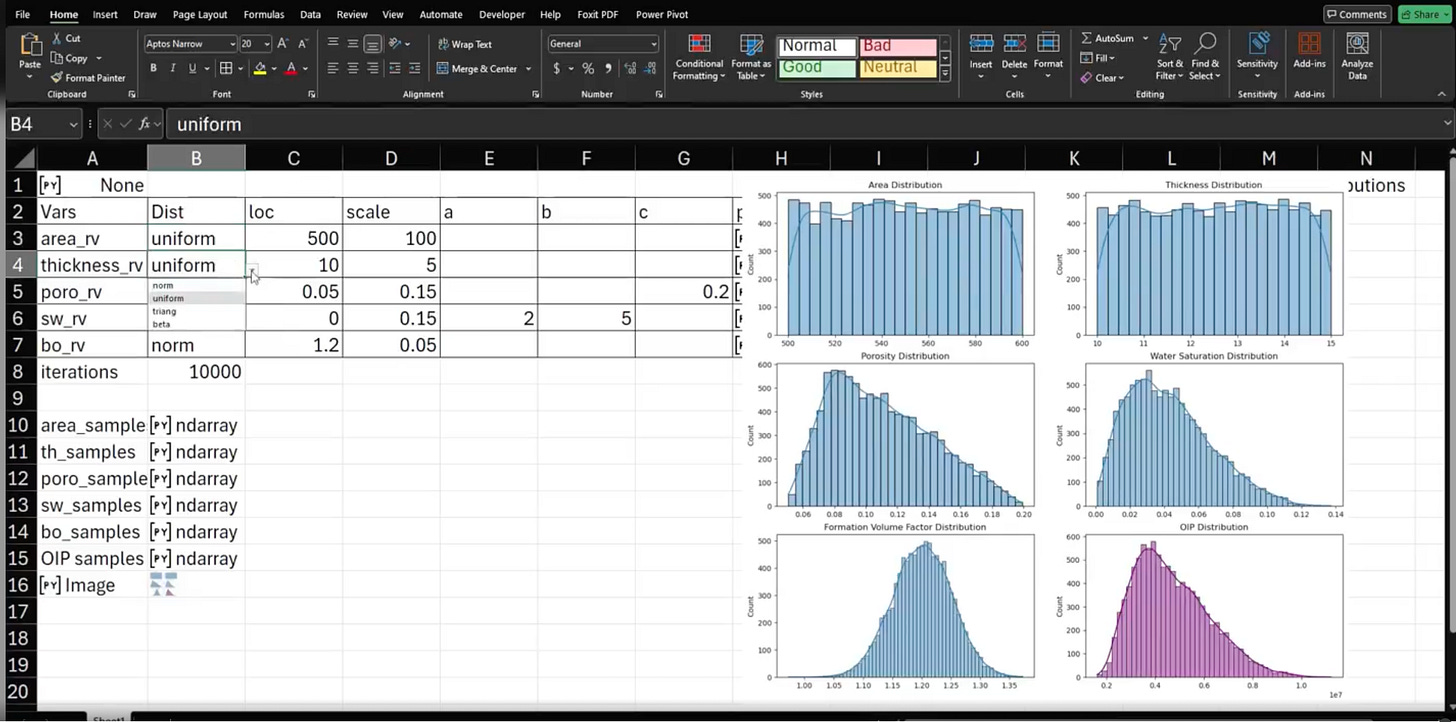
Excel just leveled up: Python is now embedded directly into the spreadsheet we know and love, transforming advanced analytics from niche to mainstream. In his latest video, Oscar Cortez shows exactly how this integration works by running a Monte Carlo simulation!
Here’s what’s exciting about Python in Excel:
Seamless Python Integration: Oscar’s Monte Carlo example highlights how you can now perform complex simulations using Python libraries like
scipy.statsright inside Excel. This matters because it puts powerful financial modeling capabilities within everyone’s reach.Expanded Flexibility: With Python libraries like
pandasandMatplotlib, users can clean, explore, and visualize data directly in Excel. Oscar’s approach shows just the beginning—this opens up endless possibilities for tailored simulations, custom visualizations, and advanced analysis.Enterprise-Level Security: Python in Excel runs securely within the Microsoft Cloud, backed by Anaconda’s enterprise-grade Python distribution. This means analysts can share their work without worrying about installations or dependencies.
What This Means for Analysts
Immediate Impact: Complex simulations like Monte Carlo can now be executed in Excel without expensive third-party tools.
Broader Analytics: Blend familiar Excel formulas with Python’s advanced functions for data visualization, predictive analytics, and beyond.
Long-Term Advantage: With this new integration, Excel has become a full-fledged analytics platform—analysts who adopt it now are ahead of the game.
Bottom Line
With Python now in Excel, you can supercharge your analytics and bring advanced simulations to life—all within the secure, collaborative Excel environment. Dive into Oscar’s video to see Monte Carlo simulations in action and imagine the possibilities for your own data.
Source: Oscar Cortez - LinkedIn
💼 Market Indicators
SPY Performance

Performance and Valuations by Region
Source: MSCI
Momentum performance by Style
Source: MSCI
S&P 500 Earnings Per Share
Source: Yardeni Research
🗺️ Around the World in Detail
United States 🇺🇸: Mixed Signals
Earnings Jump: S&P 500 earnings rose 5.1% YoY, led by strong consumer sectors, but tech giants like Meta and Microsoft fell short, raising questions about sustained growth in high-valuation stocks.
Labor Market Cooling: Job openings dropped to 7.44 million, the lowest since January 2021, while nonfarm payrolls barely grew, adding just 12,000 jobs in October. This drop signals potential slowdowns in hiring, a critical indicator as the Fed evaluates rate policy.
Manufacturing Slump: The ISM Manufacturing PMI slid to 46.5, its seventh consecutive contraction, as businesses hold back on investments amid Fed policy uncertainty. The ongoing downturn in manufacturing could influence broader economic sentiment moving forward.
International 🌐: Steady but Uneven
Canada 🇨🇦
Manufacturing PMI Up: October’s PMI climbed to 51.1, the second consecutive expansion, led by domestic demand. This return to growth in manufacturing, following 17 months of contraction, signals cautious optimism among Canadian producers.
Euro Area 🇪🇺
Resilient GDP Growth: Eurozone GDP growth doubled to 0.4% in Q3, driven by stronger-than-expected performances in Germany and France. The modest growth adds pressure on the ECB, balancing between sustaining economic recovery and controlling inflation.
Inflation at ECB Target: Inflation ticked up to 2%, driven by rising costs in food and non-energy goods. With inflation matching the ECB’s target, rate cuts may be pushed out, affecting borrowing costs and business investment.
Consumer Sentiment: Despite economic resilience, European consumer confidence remains fragile, as inflation concerns weigh on spending. Investors may expect slower retail and services growth across the bloc.
United Kingdom 🇬🇧
Budget Shifts Spur Bond Volatility: Chancellor Reeves unveiled GBP 70 billion in new spending, funded by increased taxes and borrowing, sparking bond market volatility. With higher taxes expected to slow growth, investors are watching closely for BOE rate moves.
Manufacturing Decline: October’s PMI for manufacturing fell to 49.9, signaling contraction as businesses adopt a “wait-and-see” approach amid fiscal uncertainty. The cautious outlook reflects ongoing Brexit impacts on trade and production.
Japan 🇯🇵
BoJ Holds Rates Amid Political Shifts: The Bank of Japan maintained its rate at 0.25%, aligning with a steady policy approach as the country faces post-election uncertainty. This steady stance contrasts with global tightening trends, giving Japanese equities room for potential gains.
Retail Sales Drop: Retail sales fell 2.3% in September, the steepest monthly decline since August 2021, amid inflation and fiscal concerns. The decline could weigh on Japan’s economic growth outlook heading into the end of the year.
Emerging Markets 🌏: Divergent Trends
China 🇨🇳
Stimulus Lifts Manufacturing: China’s PMI edged above 50 to reach 50.1 in October, marking a tentative recovery in manufacturing. However, export orders remain weak, reflecting ongoing global demand issues that may impact growth.
Property Sector Bright Spot: New home sales by major developers rose 7.1% YoY, the first increase in 2024, signaling stabilization efforts may be taking hold. A healthier property market could buoy broader economic sentiment, yet global investors remain cautious.
India 🇮🇳
Strong Growth Momentum: India’s manufacturing PMI remains solidly above 57, showcasing growth resilience amid global headwinds. This continued strength positions India as a regional standout, drawing investor interest in an otherwise mixed Asian outlook.
Policy Consistency Amid Growth: As inflation remains manageable, India’s steady policy path provides a stable environment for further investment. The combination of strong domestic demand and a favorable policy environment underpins India’s growth prospects as a key emerging market player.