Middle East Tensions Drive Oil Higher as U.S. Job Gains Surprise the Markets
Week Ending October 04, 2024
Welcome back to this week’s global macro update! 🌍📊 Geopolitical tensions in the Middle East sent oil prices surging, while U.S. markets showed resilience with surprise job gains fueling investor optimism. Across Europe, inflation continued its downward trend, raising hopes for policy easing, and in China, stocks soared despite ongoing economic challenges. Let's dive into how these key developments are setting the stage for market movements in the weeks ahead.
🔍 Takeaway
This week’s global macroeconomic landscape was shaped by a mix of geopolitical tensions, economic resilience, and shifting inflation dynamics. While China’s stimulus measures gave markets a boost, the U.S. job market showed surprising strength, adding complexity to the inflation outlook.
United States: Strong job gains in September propelled U.S. markets higher, overcoming concerns about Middle East tensions. However, rising wages and persistent inflation in the services sector have sparked renewed uncertainty about the Fed’s next move.
International: European markets declined, driven by escalating Middle East tensions and weakening economic activity. Inflation fell below the ECB’s 2% target, reinforcing expectations for potential rate cuts in the coming months. For investors, this could mean increased opportunities in European equities as monetary easing approaches.
Emerging Markets: China’s stimulus efforts drove a significant rally in its stock markets despite continued weakness in factory activity. Investors should be mindful of China’s long-term structural challenges, but short-term opportunities may arise as the government continues to support economic recovery.
⭐️ Post of the week
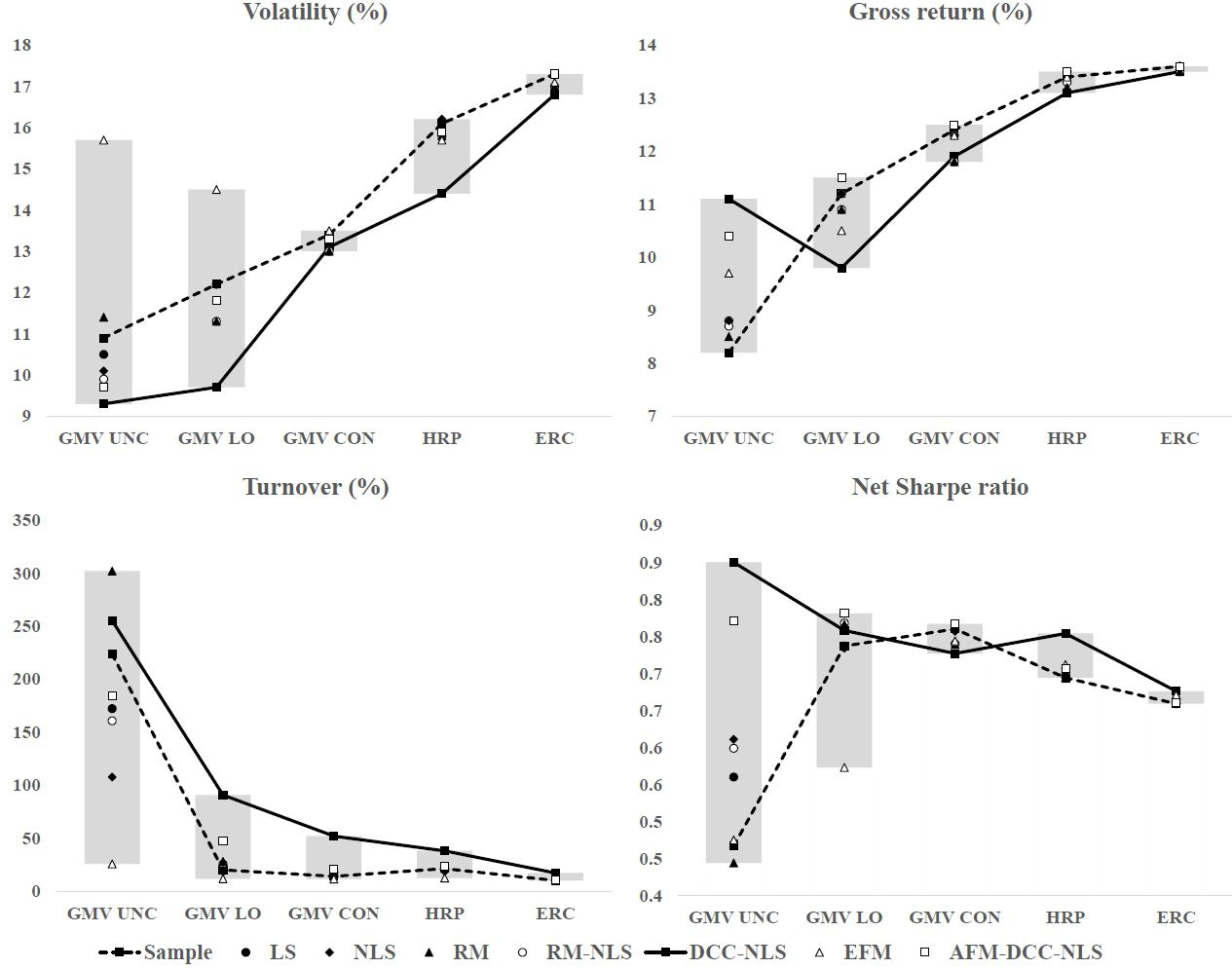
This week's chart is all about understanding how to make better investment portfolios by using variance-covariance (VCV) estimators. These estimators help us understand the risks of different assets and how they relate to each other. In the past, experts often used something called an unconstrained global minimum-variance (GMV) portfolio to try to reduce risk, but these portfolios have some big downsides—like high leverage, high concentration, and high costs—which make them unrealistic for most investors.
New research suggests that we should instead look at more practical portfolios, like those with weight limits or risk parity approaches, which are more like what investors actually use. The researchers found that adding these weight limits can naturally reduce risk without needing to use complicated methods. When they tested different types of portfolios, they saw that the extra benefits of using fancy VCV estimators mostly disappeared once you added real-world constraints. This means that what works well in theory often doesn’t have the same impact in real-life investing.
So, what's the takeaway here? If you're an investor looking to lower risk, the best approach might be to keep things simple. Using weight limits can make your portfolio more stable without needing to use overly complex models. At the end of the day, choosing tools that are both statistically reliable and easy to use in practice will give you the best chance of success.
More info at: Robeco's Insights
Source: Harald Lohre - LinkedIn
💼 Market Indicators
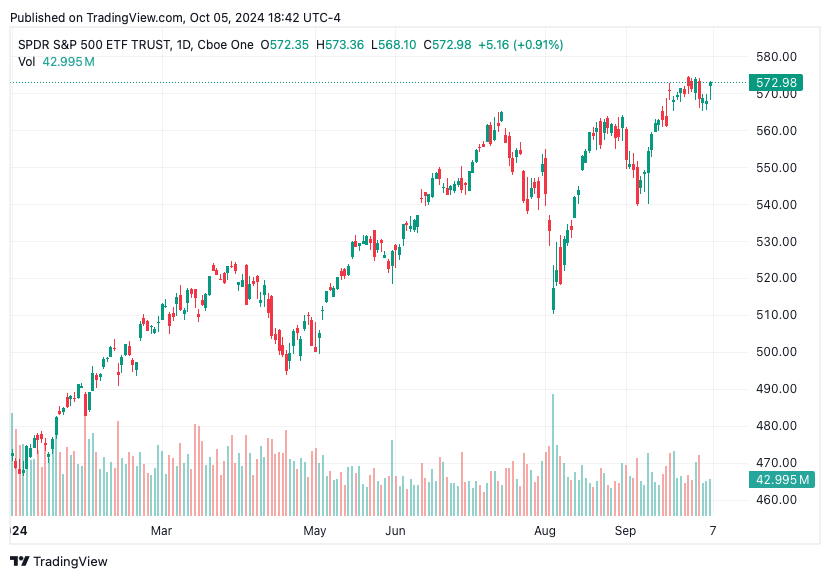
SPY Performance
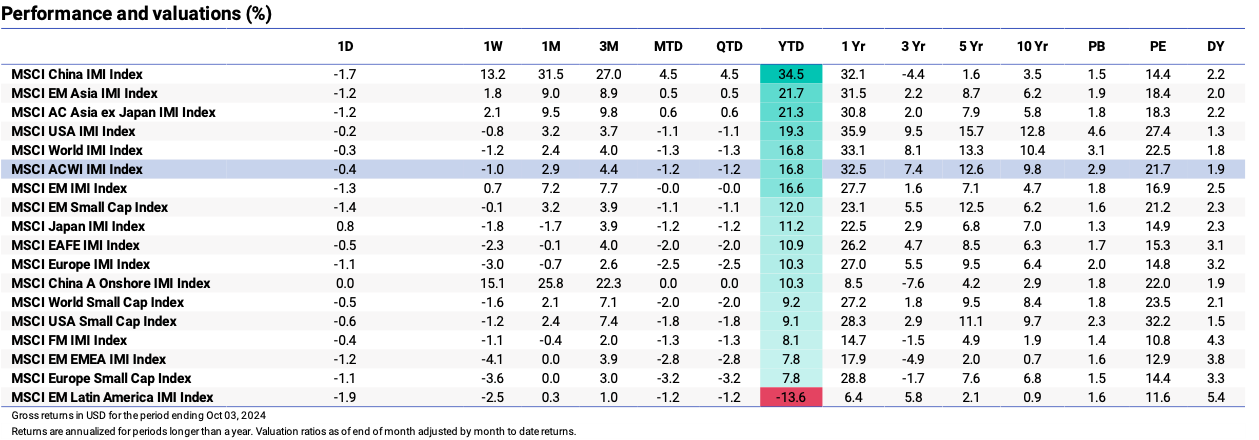
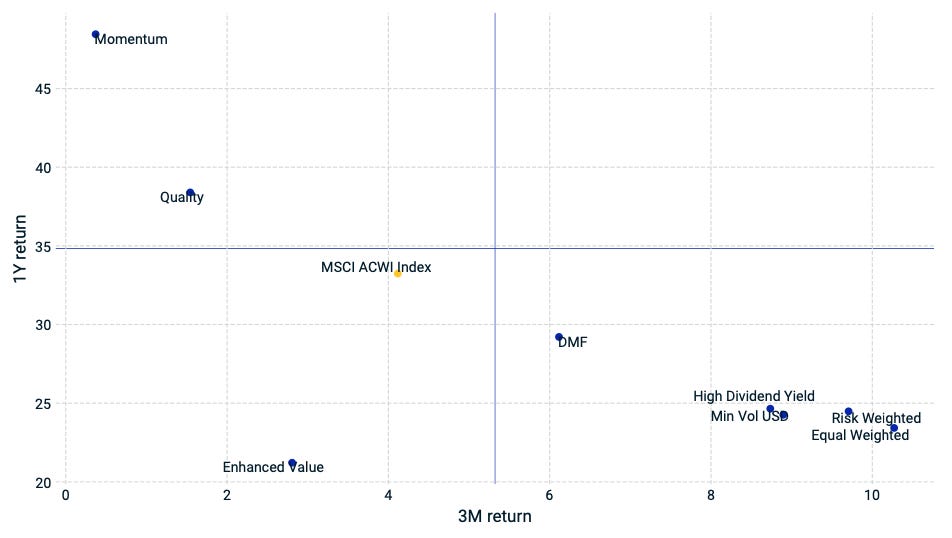
Performance and Valuations by Region
Source: MSCI
Momentum performance by Style
Source: MSCI
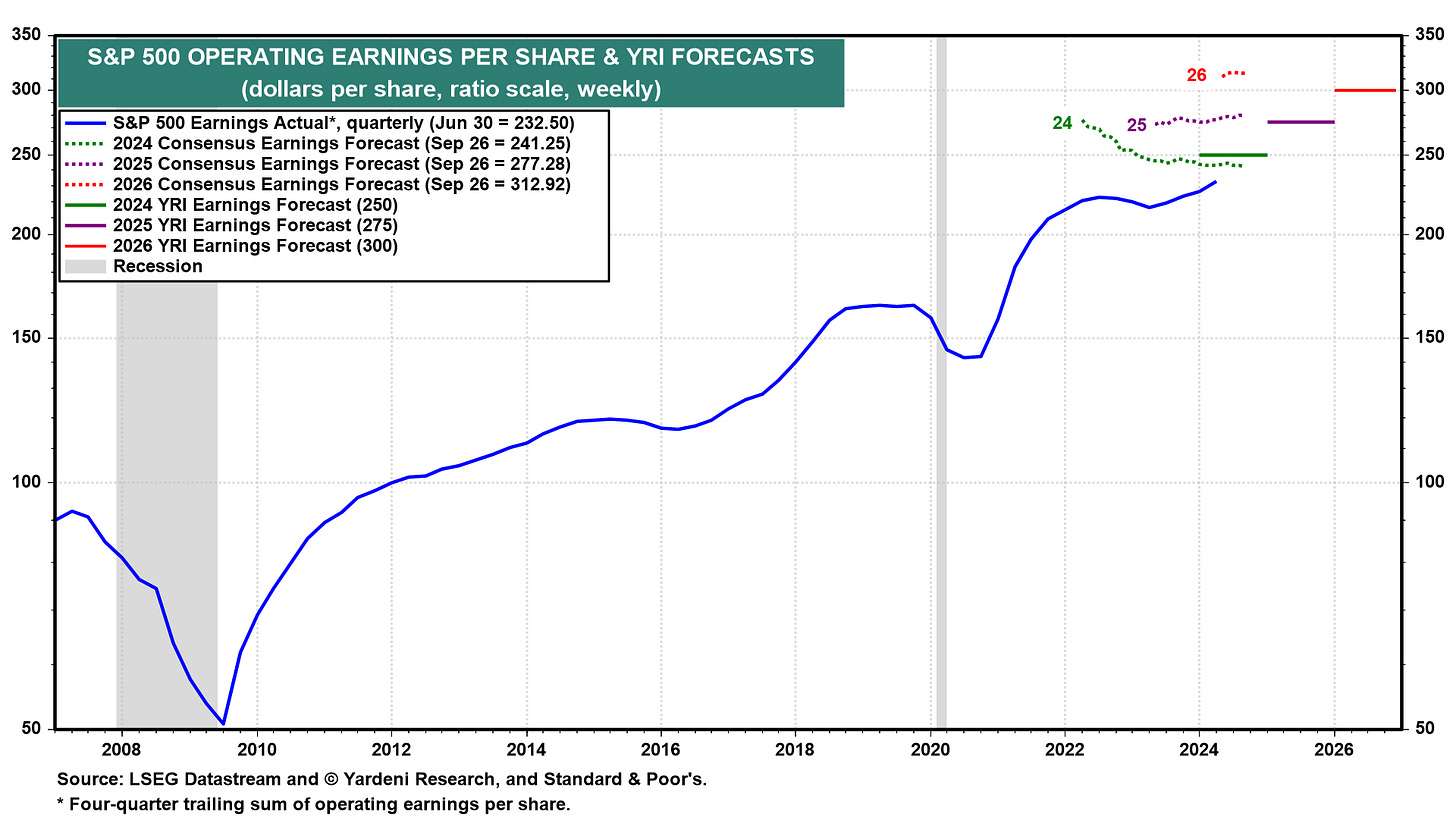
S&P 500 Earnings Per Share
Source: Yardeni Research
🇺🇸 United States: Steady Growth Amid Cooling Inflation
Nonfarm Payrolls: The U.S. added 254,000 jobs in September 2024, well above expectations, with the unemployment rate ticking down to 4.1%.
Wage Growth: Average hourly earnings rose by 0.4% in September, continuing the inflationary pressure on labor costs.
Treasury Yields: The 10-year U.S. Treasury yield spiked to 3.98%, its highest level in nearly two months, driven by strong job data.
🌐 International: Mixed Growth Across Major Economies
🇨🇦 Canada:
Manufacturing PMI: The S&P Global Manufacturing PMI rose to 50.4 in September, signaling the first improvement since April 2023, driven by better domestic demand.
Services PMI: The Services PMI fell to 46.4, marking the sharpest contraction in four months as weak demand persisted.
🇪🇺 Euro Area:
Inflation: Annual inflation in the Eurozone fell to 1.8% in September 2024, the lowest since April 2021, below the ECB’s target of 2%.
Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI): The Eurozone composite PMI was revised up to 49.6, still signaling contraction in economic activity.
🇬🇧 United Kingdom:
Services PMI: The S&P Global Services PMI fell to 52.4 in September, down from 53.7 in August, indicating a slowdown in growth, driven by weaker demand.
Manufacturing PMI: The Manufacturing PMI remained steady at 51.5, supported by domestic demand, but with slower output growth.
🇯🇵 Japan:
Stock Market: Japan’s Nikkei 225 Index fell by 3.0% following political developments, as the new Prime Minister’s hawkish stance initially spooked investors.
10-Year Yield: The yield on the 10-year Japanese government bond rose to 0.87%, tracking the rise in U.S. Treasury yields.
🌏 Emerging Markets: Policy Shifts and Economic Slowdowns
🇨🇳 China:
Stock Market Surge: Chinese stocks rallied, with the Shanghai Composite Index rising by 8.06% amid optimism over Beijing’s stimulus measures, despite factory activity contracting for the fifth consecutive month.
🇮🇳 India:
Manufacturing PMI: India’s manufacturing PMI slowed to 56.5 in September, marking the softest expansion in factory activity since January.
Services PMI: The Services PMI was revised lower to 57.7, reflecting slower growth amid rising costs.
🇰🇷 South Korea
Inflation Rate: South Korea’s inflation rate dropped to 1.6%, the lowest since February 2021, as price pressures eased, raising expectations of a rate cut by the Bank of Korea.
🇹🇼 Taiwan:
Manufacturing PMI: Taiwan’s Manufacturing PMI fell to 50.8, its lowest since April, as uncertainty over future demand weighed on output and new orders.
Stay tuned for next week's updates! Feel free to share your thoughts or questions below.